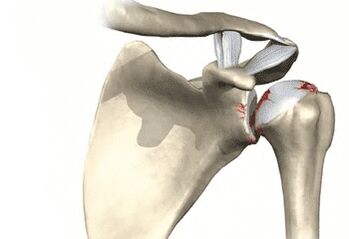
The shoulder joint is one of the most vulnerable in the human skeleton. This is due to the rather complex structure of the articulation, which is associated with a weak fixation of the scapula. Every day, the shoulder receives a heavy load during the performance of household or professional tasks. In the event of an injury, the metabolic processes are disturbed, the tissues wear out due to age - dystrophic changes begin in the cartilage tissue. This pathology is called osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
Depending on the manifestations and degree of damage to the glenohumeral joint, four degrees of pathology are diagnosed. They also differentiate between acute and chronic shoulder joint arthrosis. If the treatment is not carried out in time or in bad faith, the joint continues to deform and collapse, which ultimately leads to a significant limitation of the functions of the upper limb and loss of mobility.
Today, only grade 1 shoulder arthrosis can be completely cured. But this does not mean that you can give up and do nothing with pathology of the 2nd degree or higher. Comprehensive and adequate treatment of arthrosis of the shoulder joint by medication or surgery helps to slow down the destruction of the joint, preserve at least partial mobility of the arm and shoulder, and prevent disability.
Symptoms and causes
Deforming arthrosis of the shoulder joint does not develop in a day. At first, the changes are minor. Cartilage gradually loses its elasticity under the influence of various factors - these can be age-related changes or disruption of tissue metabolism. Microcracks appear on its surface, in which calcium salts accumulate. Then it thins, becomes brittle, and collapses.
This process is often accompanied by inflammation, which spreads to the surrounding muscle, connective and bone tissues. This manifests primarily as pain - at first a minor pain. Then they become more intense and never go away in an advanced stage, which significantly reduces a person's performance and quality of life.
The main causes of DOA of the shoulder joint are as follows:
- Impaired blood circulation in the cartilaginous tissues of the shoulder in atherosclerosis and other chronic diseases related to blood vessels.
- Chronic pathologies of an autoimmune nature, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus).
- Congenital disorders of the shoulder joint, birth injuries in infants and other injuries that lead to pathological deformation and dysfunction of the limb.
- Pathologies of joint structures acquired after an injury or accident, unsuccessful surgery, including arthritis, arthritis, osteoporosis, etc.
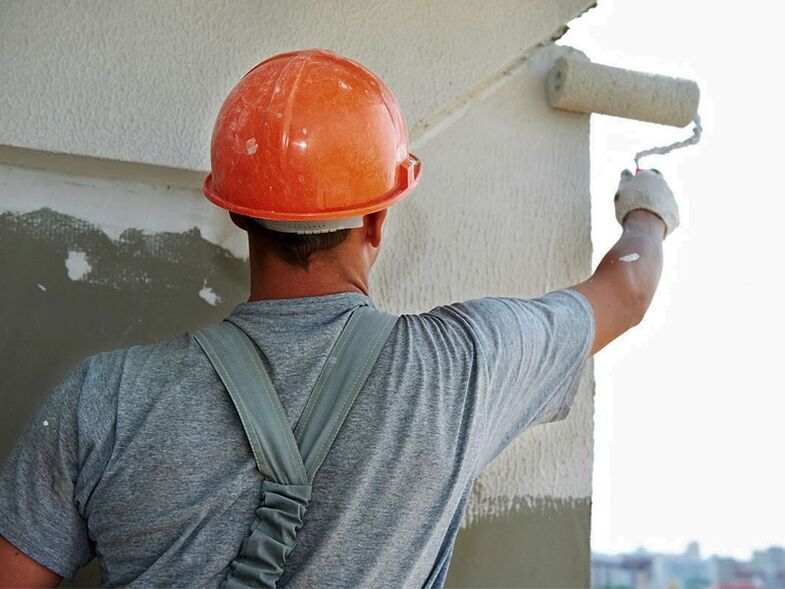

In addition, there are provoking factors that increase the risk of developing shoulder joint arthrosis several times over. These include:
- professional activity in which the shoulder joint receives a heavy load every day for many years - the shoulder joint is quite rightly called the disease of plasterers, painters and loaders;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity - with insufficient exercise, blood circulation slows down, joint tissues do not receive the necessary amount of nutrients and begin to atrophy;
- overweight - often combined with the previous factor; with obesity, a person cannot move actively, while the joints receive additional stress due to extra pounds;
- hereditary predisposition;
- old age - about 80% of people over the age of 70 have symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Most often, when examining and interviewing the patient, the doctor identifies a combination of several diseases and provoking factors. A typical patient diagnosed with arthrosis of the shoulder joint is a man or woman over 50 years of age who does heavy physical work, is overweight and suffers from other chronic pathologies (diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, varicose veins, knee arthritis, etc. ). In this case, changes in the right shoulder occur more often than the left. This is due to the fact that most people actively use their right hand at work and at home, with the exception of congenital left-handers.
How to recognize the disease
Symptoms of arthrosis of the shoulder joint may not appear for a long time. If your shoulder starts to hurt from time to time, you attribute it to fatigue, take painkillers, use a warming ointment, and calm down. But sooner or later, the time comes when pills and ointments no longer help, the pain becomes constant, intense and bothers me even at rest and at night. In addition to this symptom, the following signs indicate dystrophic changes in the shoulder joint:
- swelling and deformation of the joint, visible to the naked eye;
- redness over the joint, local temperature increase;
- characteristic cracking in the joint. The creaking sounds that occur during sharp movements of the hand can be explained by the accumulation of salts in the cracks of the cartilage and between the joint elements. At first, the crunching occurs only with sudden movements, it is soft and barely audible. In advanced forms of the disease, the shoulder cracks with every movement, the sound is heard by others;
- limitation of limb mobility. When examining the patient, the doctor asks him to comb his hair. This examination is sufficient to diagnose arthrosis of the shoulder joint: the patient will feel a sharp pain, make a rotating movement with the shoulder, it will be difficult to move the shoulder back, the doctor will hear a crack and a click in the joint.
DOA of the shoulder must be treated or over time the patient will lose full mobility and performance of the upper extremity. If the process of destruction of the cartilage and surrounding tissues has already begun, it will not stop by itself. Proper nutrition, folk remedies, a healthy lifestyle and exercise are not enough here. In order to treat the problem and prevent disability, a complex treatment will be required using various drugs and physical procedures.
degrees
DOA of the shoulder joint has several stages, each of which manifests itself differently and requires a different approach to treatment.
- Grade 1.At this stage, the disease is just beginning to develop, the changes in the cartilage tissue are still minor. The main symptoms of grade 1 DOA are joint and limb weakness and intermittent nagging pain. The pain appears after physical exertion, during monotonous, long-lasting repetitive hand movements. After a night's sleep or a long rest, a person feels stiffness in the shoulder joint, but as it develops, the stiffness still goes away without drugs or physical procedures - a light warm-up is enough. If you take an X-ray at this stage, the image will not show significant changes in the joint structures, although thinning and deformation of the cartilage may be noticeable.
- Grade 2.The pathological process proceeds more actively and manifests itself. People are already used to the fact that their shoulders will hurt after work, they "wait" for the pain, there is a painkiller, an ointment for joint pain, pharmacy or homemade, that's it. X-ray diagnostics shows noticeable changes in the joint: thinning and deformation of the cartilage, inflammation of the joint membraneThe joint sometimes becomes red, swollen, and you can hear crunching, creaking, clicking during movement.
- Grade 3.The shoulder joint constantly hurts and crunches, in order to reduce the discomfort, the person tries not to touch it and does not move the limb at all. The deformation is visually noticeable, the size and shape of the affected shoulder differs from the healthy one, it often becomes red and swollen, which is associated with increased pain. They cannot be removed with painkillers.
If nothing happens in the third stage of the disease, then the fourth stage occurs - complete immobility of the shoulder joint and limb. In this case, it is pointless to prescribe medicine and physiotherapy, only endoprosthesis surgery helps to at least partially restore the functionality of the hand. But even that doesn't always work out.
Comment:Grade 3 shoulder arthrosis is extremely rare in medical practice. Typically, the patient seeks medical help earlier and begins treatment. Severe cartilage destruction can occur as a result of extensive trauma, if the patient was unable to see a doctor for some reason, or lives in disadvantaged social conditions where a qualified doctor is not available.
How is arthrosis diagnosed and treated?
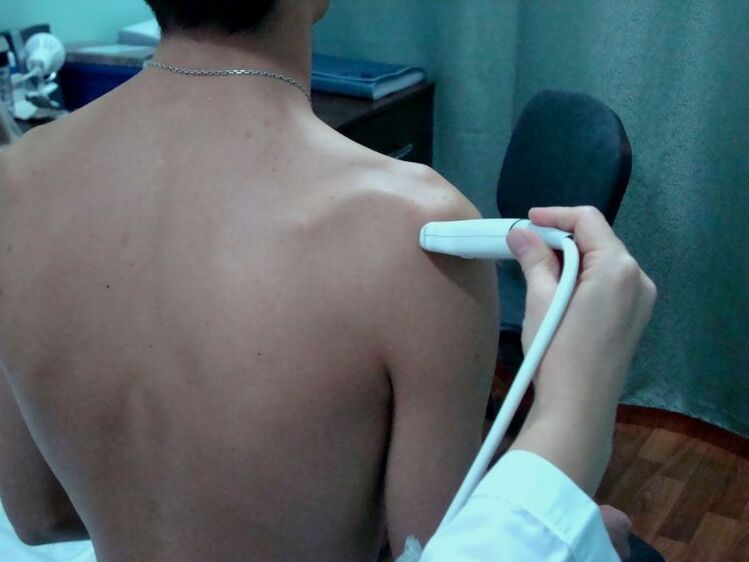
A good doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis after a conversation with the patient and an external examination. In order to exclude or identify other pathologies and complications, more instrumental diagnostic methods are needed. The following diagnostic measures should be performed to determine how severely the joint is affected and whether inflammation is occurring:
- x-ray;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- in some cases, ultrasound to get a complete picture of the state of the joint;
- clinical urine and blood tests - the number of leukocytes and the sedimentation rate of red blood cells are evaluated. If they are too high, an inflammatory process develops in the body.
The best way to treat pathology is determined by the doctor individually, taking into account the age, occupation and general condition of the patient.
Traditional treatment includes the following methods and tools:
- Therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines are prescribed in the form of tablets or powders for oral administration, or in the form of ointments for external use to eliminate the main symptoms of inflammation - pain, swelling, redness, increased body temperature.
- Anesthetics for the treatment of severe pain in the form of tablets or injections. These drugs cannot be taken continuously, they do not eliminate the cause of the disease, and only in extreme cases when the pain is unbearable.
- Chondroprotectors - drugs that promote the restoration of cartilage tissue and prevent further destruction. They partially relieve pain and swelling, as well as deformity of the shoulder joint. Such drugs do not work immediately, they must be taken for at least 3-4 months.
- A course of muscle relaxants - pills or injections that relax muscle spasms. These are optional drugs in the complex treatment of osteoarthritis, they are not always prescribed.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements with collagen and hyaluronic acid.
In order to increase the effectiveness of the treatment, speedy recovery and prevent new lesions, a special therapeutic diet is also prescribed. The patient's diet includes foods rich in vitamins B, A, C, E - fresh fruits and vegetables, any kind of cabbage, cereals, legumes. Polyunsaturated fatty acids can be obtained from marine fish and seafood. The gelatin diet is practiced because gelatin helps to restore the elasticity of cartilage tissue. The menu includes jellied meats made from beef legs and tails, aspic and various jellies. It is useful to take gelatin in its pure form, previously soaked in warm water.
Physiotherapy is the next important point in the complex treatment of shoulder arthritis. They are started only when the inflammatory process stops. Depending on the degree, dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of drug treatment, the doctor selects a combination of the following physical procedures:
- cryotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnet therapy;
- mud therapy;
- various types of massages;
- physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy procedures are aimed at activating metabolic processes in the joint tissues, normalizing blood circulation and restoring limb mobility. With their help, the number and dosage of drugs taken can be reduced, which is especially valuable if the pathology is detected in a teenager, an elderly person or a lactating woman.
Useful advice:Grade 1-2 lesions of the shoulder joint can be treated at home, with the additional use of folk remedies. The main thing is that the patient does not forget to take the medicines on time and does not miss the physical procedures - the effect will be noticeable and lasting only if all the prescriptions of the doctor are followed regularly and conscientiously.

If conservative treatment is ineffective, the doctor is forced to recommend surgery to the patient. The remains of the damaged joint are removed and a prosthesis is implanted in its place. Such an intervention is not rare, but it requires highly trained doctors, precision and attention at all stages. In addition, prostheses do not always take root well, and the recovery period after surgery lasts at least six months. Therefore, if you notice that your shoulder regularly starts to hurt, pulls, goes numb, or hears a creaking sound when you move, do not postpone a doctor's visit, get a timely examination and, if necessary, start treatment.
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is a fairly common pathology of the musculoskeletal system, mainly occurring in people over 50 years of age. The pathology develops gradually, little by little, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the joint structures begin to collapse, which manifests itself in pain, swelling, and joint stiffness. In the early stages of the disease, the progression of the disease can be stopped with the help of comprehensive treatment: medicines, vitamin supplements, diet and physical therapy. Advanced osteoarthritis can only be treated surgically.































